I've moved this blog to Wordpress platform. Go check it out as it will have lots and lots of newer materials and blog posts, as well as all the blog posts from this site. So the newer site is bigger and better.
Go to - www.oralytics.com
I've moved this blog to Wordpress platform. Go check it out as it will have lots and lots of newer materials and blog posts, as well as all the blog posts from this site. So the newer site is bigger and better.
Go to - www.oralytics.com
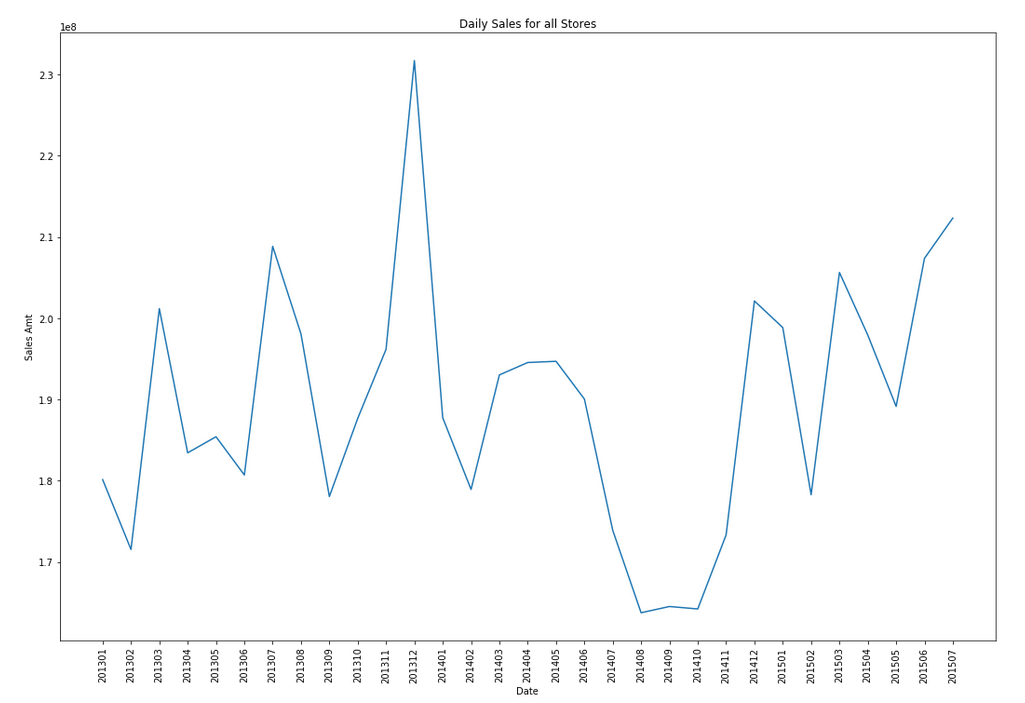
-- Create input time series create or replace view demo_ts_data as select to_date(to_char(sales_date, 'MON-RRRR'),'MON-RRRR') sales_date, sum(sales_amt) sales_amt from demo_time_series group by to_char(sales_date, 'MON-RRRR') order by 1 asc;
CREATE TABLE demo_ts_settings(setting_name VARCHAR2(30),
setting_value VARCHAR2(128));
BEGIN
-- delete previous setttings
delete from demo_ts_settings;
-- set ESM as the algorithm
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.algo_name,
dbms_data_mining.algo_exponential_smoothing);
-- set ESM model to be Holt-Winters
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_model,
dbms_data_mining.exsm_holt);
-- set interval to be month
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_interval,
dbms_data_mining.exsm_interval_month);
-- set prediction to 4 steps ahead
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_prediction_step,
'4');
commit;
END;
Now we can call the function, generate the model and produce the predicted values.BEGIN
-- delete the previous model with the same name
BEGIN
dbms_data_mining.drop_model('DEMO_TS_MODEL');
EXCEPTION
WHEN others THEN null;
END;
dbms_data_mining.create_model(model_name => 'DEMO_TS_MODEL',
mining_function => 'TIME_SERIES',
data_table_name => 'DEMO_TS_DATA',
case_id_column_name => 'SALES_DATE',
target_column_name => 'SALES_AMT',
settings_table_name => 'DEMO_TS_SETTINGS');
END;
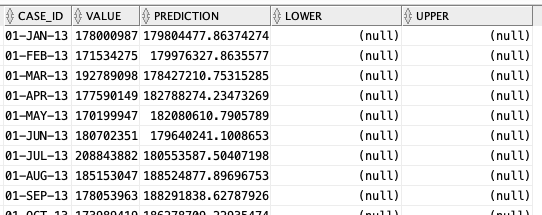
-- get predictions select case_id, value, prediction, lower, upper from DM$VPDEMO_TS_MODEL order by case_id;
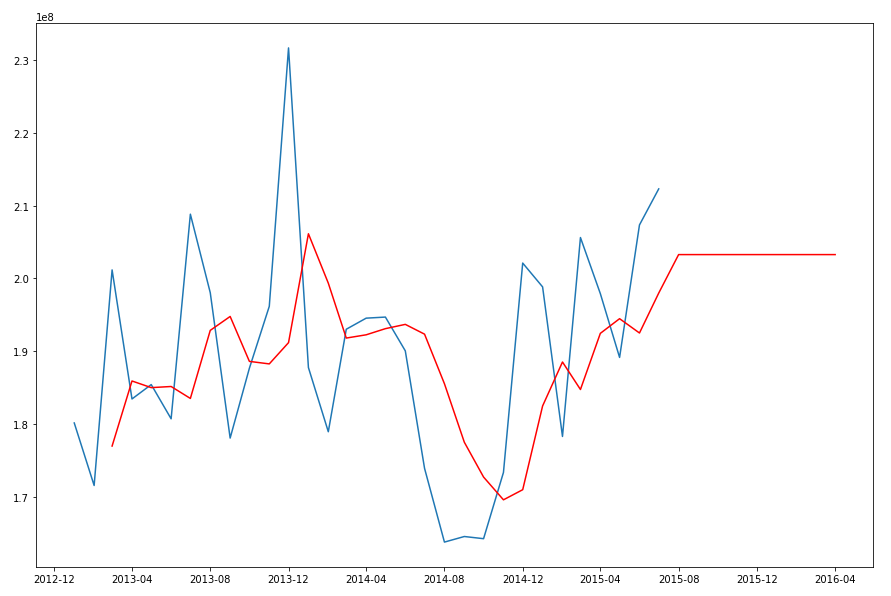
 The blue line contains the original data values and the red line contains the predicted values. The predictions are very similar to those produced using Holt-Winters in Python.
The blue line contains the original data values and the red line contains the predicted values. The predictions are very similar to those produced using Holt-Winters in Python.
BEGIN
-- delete previous setttings
delete from demo_ts_settings;
-- select ESM as the algorithm
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.algo_name,
dbms_data_mining.algo_exponential_smoothing);
-- set ESM model to be Holt-Winters Seasonal Adjusted
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_model,
dbms_data_mining.exsm_HW_ADDSEA);
-- set interval to be month
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_interval,
dbms_data_mining.exsm_interval_month);
-- set prediction to 4 steps ahead
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_prediction_step,
'4');
-- set seasonal cycle to be 5 quarters
insert into demo_ts_settings
values (dbms_data_mining.exsm_seasonality,
'5');
commit;
END;
BEGIN
-- delete the previous model with the same name
BEGIN
dbms_data_mining.drop_model('DEMO_TS_MODEL');
EXCEPTION
WHEN others THEN null;
END;
dbms_data_mining.create_model(model_name => 'DEMO_TS_MODEL',
mining_function => 'TIME_SERIES',
data_table_name => 'DEMO_TS_DATA',
case_id_column_name => 'SALES_DATE',
target_column_name => 'SALES_AMT',
settings_table_name => 'DEMO_TS_SETTINGS');
END;

data()
from sklearn import datasets


# perform some Statistics on the items in a panda
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as plt
videoReview = pd.read_csv('/Users/brendan.tierney/Downloads/Video_Games_Sales_as_at_22_Dec_2016.csv')
videoReview.head(10)
videoReview.dtypes
df = videoReview.select_dtypes(include=['object']).copy() df.head(10)
df.dropna(inplace=True) df.isnull().sum()
df.describe()
#check the number of passengars for each variable import seaborn as sb import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 10, 8 sb.countplot(x='Platform',data=df, palette='hls')
sb.countplot(x='Genre',data=df, palette='hls')
sb.countplot(x='Rating',data=df, palette='hls')
#apply one-hot-coding to all the categorical variables # and create a new dataframe to store the results df2 = pd.get_dummies(df) df2.head(10)
df['Rating'].value_counts()
find_replace = {"Rating" : {"E": 1, "T": 2, "M": 3, "E10+": 4, "EC": 5, "K-A": 5, "RP": 5, "AO": 5}}
df.replace(find_replace, inplace=True)
df.head(10)
sb.countplot(x='Rating',data=df, palette='hls')
#let's check the data types again df.dtypes
df["Platform_Category"] = df["Platform"].astype('category')
df.dtypes
df["Platform_Category"] = df["Platform_Category"].cat.codes df.head(20)
df.groupby("Platform")["Platform"].count()
#Let's use the fit_tranforms function to encode the Genre variable from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder le_make = LabelEncoder() df["Genre_Code"] = le_make.fit_transform(df["Genre"]) df[["Genre", "Genre_Code"]].head(10)
df.groupby("Genre_Code")["Genre_Code"].count()
df.head(10)
df = df.drop('Genre', axis=1)
df.head(10)
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer lb_style = LabelBinarizer() lb_results = lb_style.fit_transform(df["Rating"]) lb_df = pd.DataFrame(lb_results, columns=lb_style.classes_) lb_df.head(10)