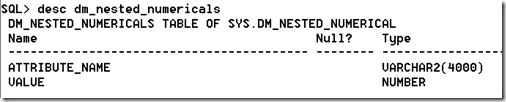
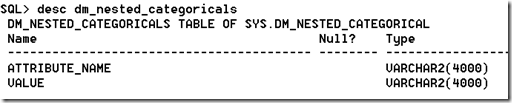
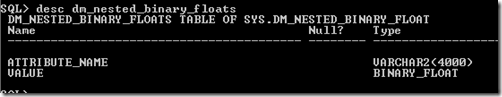
Oracle Open World 13 finished up last Thursday and I’ve send most of the time since either traveling back to Ireland, trying to re-adjust to Irish time and most importantly spending some time with the family.
I want to use this blog post to say ‘thank you’ to a large number of people. I will have another blog post on some of the important announcements (for me) at Oracle Open World.
I had 2 presentations at OOW and I also assisted at a hands-on lab. These were spread out over Monday to Wednesday, with one presentation/lab on each day. It was fun and many thanks to the people who came to these sessions. I had many conversations during the remainder of OOW with some of the people who attended my sessions.
I would like to thank Lillian, Vikki and all the OTN team for making all the arrangements, organizing events and lots and lots of things that happened at OOW. The Oracle ACE Programme paid for my flights and accommodation while I was at the ACE Directors briefing at Oracle HQ before OOW and during OOW.
I’ve heard stories about the ACE Directors briefing over the years. This year was my first one and all I can say is that it lived up to the stories and more. Over 2 (long-ish) days we had a number of SVPs, VPs, and other very senior people from various divisions of Oracle come into the briefing and openly tell us what is happening with the products, what will be announced at OOW and what will be coming over the next 6 to 12 months. They told us all of this under NDA, so we cannot talk about any of it until Oracle has publically announced it. We also had Thomas Kurian EVP talk to us for just over an hour. He was very impressive. In my next blog post I will talk about some of the announcements that were made during OOW.
Thank you to DIT for making the necessary arrangements and facilitating me to be away for this prolonged trip.
There were many social events during OOW and on some evening there was 3 different events for me to go to. Unfortunately I wasn’t able to get to all of them. I met up with lots of people from countries like Norway, Belgium, Holland, UK, Austria, Australia, Canada, Brazil, Ireland and the USA. Many thanks to RittmanMead and Peak Indicators for the meals, and lots of user groups and various Oracle countries for the drinks.
On my last night at OOW I went to my first baseball game between the Giants and the Dodgers, with Roel Hartman from Holland. This was a great night of entertainment and I would highly recommend going to a baseball game. The Giants won.
As always I’m sure that I have missed some people off this list. I do apologise and I’ll blame the jet lag for it
OOW is great for all the conference swag you can get. I tried not to get too carried away with it, but the photographs below will give you some idea of what I collected.


![clip_image002[11] clip_image002[11]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi_GBa_AZLuiKtkwxe6zECZXkMShFuSQVDnyBHYrGFs-bSj9y-e1Mrd0HhYk6EU9iB1wO1PAob4x6P_p8OG8VRWXNa8U-tNpCk0RFeghjq8H9ec0Zk57FYJKOv3sFUv0vaJnvFk01jp-QUN/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[13] clip_image002[13]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjiN-sM4i8lJrw3oJdXFQKz4n0cVG8UIYxl8Vxuj5nfDA-S3x91K3rtM6Jr72VkFbHn0IAg7swXQnBsB6LyCLLkcj7n7TqsrsP0Hzb5pkQ-veD2ZS2WaYBJThwMzzdnPUqF0n3hiI8V5NBY/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[9] clip_image002[9]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiuoqPATupnqs1kDWqbEBQy_JlsP8PH5I6yjJRYtv8P6_S_H-9rjutaCkg2LQcYbNhO4WhXplz84UtzCTcyQi8KZVOm2cNv7kidCmx-y2YAtRd3MdPiQOBh28yhS6YZ42pYdLP6PuF2RBff/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiO_W05BeuLSrGKkGcRcogphB9DoKY4Q_bgee6qqK7hzrfCtgXJ0L9hZ22d7IXHSc8j5tFVKQE6m6SUGljOp5R8n5a-nImCuKSp42l4ArgoKALEVtwWSxKYeE8u1ibeYFDfv8e4mXB95Das/?imgmax=800)