A couple of days ago it was announced that several Oracle images were available on the Docker Store.
This is by far the easiest Oracle Database install I have every done !
You simply have no excuse now for not installing and using an Oracle Database. Just go and do it now!
The following steps outlines what I did you get an Oracle 12.1c Database.
1. Download and Install Docker
There isn't much to say here. Just go to the Docker website, select the version docker for your OS, and just install it.
You will probably need to create an account with Docker.

After Docker is installed it will automatically start and and will be placed in your system tray etc so that it will automatically start each time you restart your laptop/PC.
2. Adjust the memory allocation
From the system tray open the Docker application. In the Advanced section allocate a bit more memory. This will just make things run a bit smoother. Be a bit careful on how much to allocate.

In the General section check the tick-box for automatically backing up Docker VMs. This is assuming you have back-ups setup, for example with Time Machine or something similar.
3. Download & Edit the Oracle Docker environment File
On the Oracle Database download Docker webpage, click on the the Get Content button.

You will have to enter some details like your name, company, job title and phone number, then click on the check-box, before clicking on the Get Content button. All of this is necessary for the Oracle License agreement.
The next screen lists the Docker Services and Partner Services that you have signed up for.
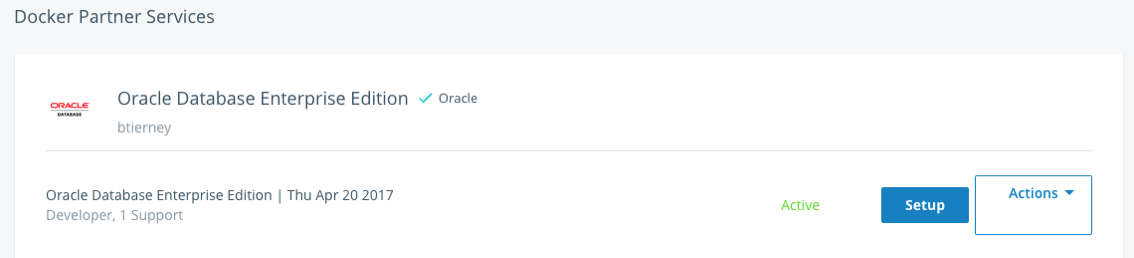
Click on the Setup button to go to the webpage that contains some of the setup instructions.
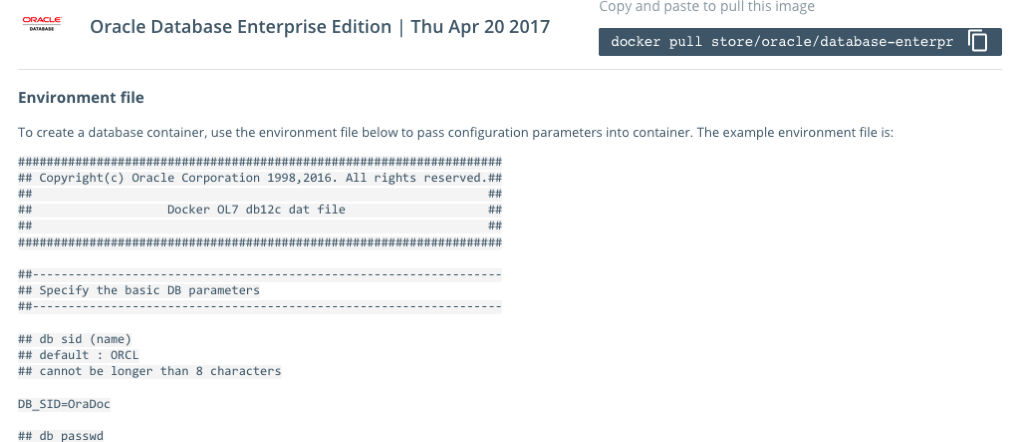
The first thing you need to do is to copy the sample Environment File. Create a new file on your laptop/desktop and paste the environment file contents into the file. There are a few edits you need to make to this file. The following is the edited/modified Environment file that I created and used. The changes are for DB_SID, DB_PASSWD and DB_DOMAIN.
####################################################################
## Copyright(c) Oracle Corporation 1998,2016. All rights reserved.##
## ##
## Docker OL7 db12c dat file ##
## ##
####################################################################
##------------------------------------------------------------------
## Specify the basic DB parameters
##------------------------------------------------------------------
## db sid (name)
## default : ORCL
## cannot be longer than 8 characters
DB_SID=ORCL
## db passwd
## default : Oracle
DB_PASSWD=oracle
## db domain
## default : localdomain
DB_DOMAIN=localdomain
## db bundle
## default : basic
## valid : basic / high / extreme
## (high and extreme are only available for enterprise edition)
DB_BUNDLE=basic
## end
I called this file 'docker_ora_db.txt'
4. Download and Configure Oracle Database for Docker
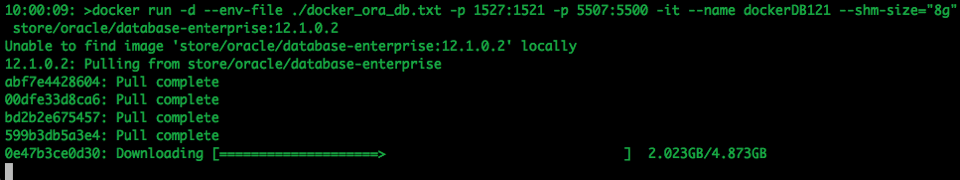
The following command will download and configure the docker image
$ docker run -d --env-file ./docker_ora_db.txt -p 1527:1521 -p 5507:5500 -it --name dockerDB121 --shm-size="8g" store/oracle/database-enterprise:12.1.0.2
This command will create a container called 'dockerDB121'. The 121 at the end indicate the version number of the Oracle Database. If you end up with a number of containers containing different versions of the Oracle Database then you need some way of distinguishing them.
Take note of the port mapping in the above command, as you will need this information later.
When you run this command, the docker image will be downloaded from the docker website, will be unzipped and the container setup and ready to run.
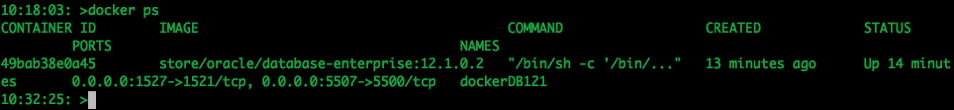
5. Log-in and Finish the configuration
Although the docker container has been setup, there is still a database configuration to complete. The following images shows that the new containers is there.
To complete the Database setup, you will need to log into the Docker container.
docker exec -it dockerDB121 /bin/bash
Then run the Oracle Database setup and startup script (as the root user).
/bin/bash /home/oracle/setup/dockerInit.sh

This script can take a few minutes to run. On my laptop it took about 2 minutes.
When this is finished the terminal session will open as this script goes into a look.
To run any other commands in the container you will need to open another terminal session and connect to the Docker container. So go open one now.
6. Log into the Database in Docker
In a new terminal window, connect to the Docker container and then switch to the oracle user.
su - oracle
Check that the Oracle Database processes are running (ps -ef) and then connect as SYSDBA.
sqlplus / as sysdba
Let's check out the Database.
SQL> select name,DB_UNIQUE_NAME from v$database;
NAME DB_UNIQUE_NAME
--------- ------------------------------
ORCL ORCL
SQL> SELECT v.name, v.open_mode, NVL(v.restricted, 'n/a') "RESTRICTED", d.status
FROM v$pdbs v, dba_pdbs d
WHERE v.guid = d.guid
ORDER BY v.create_scn;
NAME OPEN_MODE RES STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- --- ---------
PDB$SEED READ ONLY NO NORMAL
PDB1 READ WRITE NO NORMAL
And the tnsnames.ora file contains the following:
ORCL = (DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 0.0.0.0)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = ORCL.localdomain) ) )
PDB1 = (DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 0.0.0.0)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = PDB1.localdomain) ) )
You are now up an running with an Docker container running an Oracle 12.1 Databases.
7. Configure SQL Developer (on Client) to access the Oracle Database on Docker
You can not use your client tools to connect to the Oracle Database in a Docker Container. Here is a connection setup in SQL Developer.
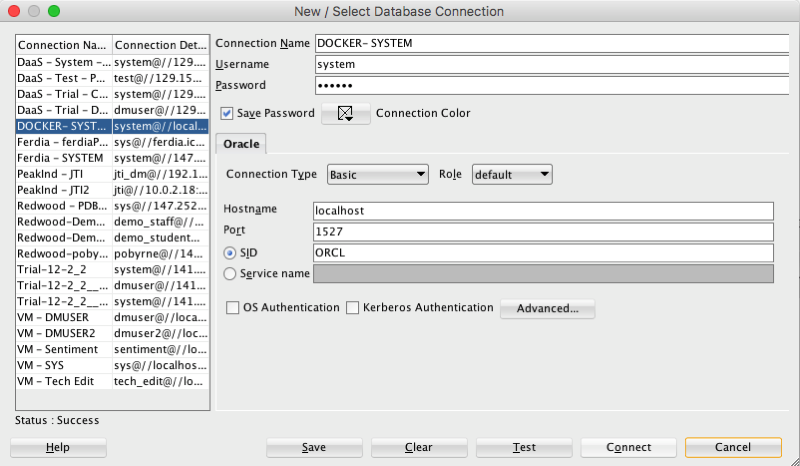
Remember that port number mapping I mentioned in step 4 above. See in this SQL Developer connection that the port number is 1527.
Thats it. How easy is that. You now have a fully configured Oracle 12.1c Enterprise Edition Database to play with, to have fun and to explore all the wonderful features of the Oracle Database.













